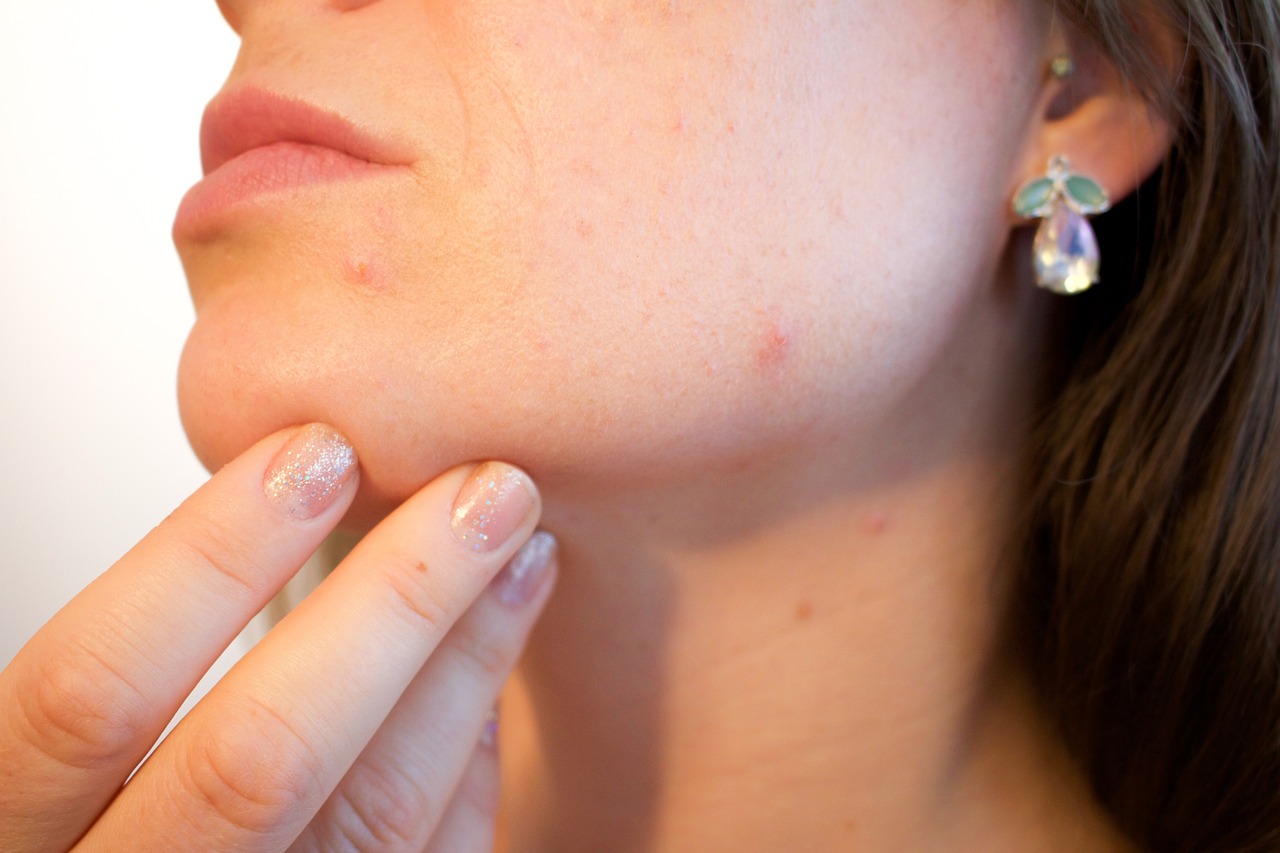
If you’ve ever experienced mysterious bites on your skin that seem to appear out of nowhere, you may be dealing with a bed bug infestation. These tiny, parasitic insects have been plaguing humans for centuries, and their impact on our dermatological health is a cause for concern.
In this article, we will explore the role bed bugs play in dermatological conditions, shedding light on the mechanisms behind their bites, the potential for allergic reactions, and the association with skin infections and dermatitis.
Bed bug bites are not only annoying and itchy but can also lead to significant skin irritation and discomfort. Understanding the nature of these bites is crucial in recognizing and addressing the problem.
Additionally, some individuals may develop allergic reactions to bed bug bites, exacerbating the already unpleasant symptoms. Skin infections are another potential consequence of bed bug infestations, as the insects can introduce bacteria into the skin through their bites.
Furthermore, the presence of bed bugs has been linked to the development of dermatitis, a chronic condition characterized by inflammation and itching of the skin.
To prevent the negative effects of bed bug infestations on our dermatological health, it is essential to be knowledgeable about their habits and behaviors. By following evidence-based strategies, such as regular inspection of your sleeping area and practicing proper hygiene, you can minimize the risk of bed bug bites and their associated dermatological conditions.
It’s time to unmask the role of bed bugs in dermatology and take proactive measures to protect our skin from these pesky pests.
Understanding Bed Bug Bites
If you’re experiencing itchy red welts on your skin, you might be tempted to think that bed bug bites are the cause, but it’s important to remember that not all skin reactions are a result of bed bugs.
Bed bug bites typically appear as small, red, raised bumps on the skin that are often accompanied by intense itching. These bites are usually found in a linear pattern or grouped together in clusters.
It’s crucial to note that bed bug bites can be easily misdiagnosed as other insect bites or skin conditions, such as mosquito bites or eczema.
To determine if your skin reaction is truly due to bed bugs, it’s recommended to consult a dermatologist who can examine your skin and gather any necessary evidence, such as identifying the presence of bed bugs or their fecal matter.
Allergic Reactions to Bed Bugs
Be aware that allergic reactions to these pests can cause intense itching and discomfort, leaving you feeling frustrated and desperate for relief. When bed bugs bite, they inject saliva into your skin, which contains substances that can trigger an allergic response in some individuals.
The allergic reaction can vary from person to person, but common symptoms include redness, swelling, and itching at the site of the bite. In more severe cases, individuals may experience blistering, hives, or even respiratory symptoms such as wheezing or difficulty breathing.
Allergic reactions to bed bug bites are often delayed, with symptoms appearing hours or even days after the initial bite. It is important to seek medical attention if you suspect an allergic reaction, as treatment options, such as antihistamines or corticosteroids, can provide relief and help manage the symptoms.
Bed Bugs and Skin Infections
Skin infections can develop as a result of bed bug bites, causing additional discomfort and irritation. When bed bugs bite, they inject saliva into the skin to prevent blood clotting. This saliva contains various proteins and enzymes that can trigger an immune response in some individuals, leading to an allergic reaction.
However, the constant itching and scratching of bed bug bites can create breaks in the skin, making it susceptible to secondary bacterial infections. Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus pyogenes are common bacteria that can cause skin infections. These infections can result in symptoms such as redness, swelling, warmth, and pus-filled blisters.
In severe cases, cellulitis or impetigo can develop, requiring medical treatment with antibiotics. Therefore, it’s important to address bed bug infestations promptly to prevent skin infections and associated complications.
Bed Bugs and Dermatitis
In this discussion, you’ll gain a comprehensive understanding of dermatitis caused by bed bug infestations. You’ll learn how to identify the symptoms and triggers of bed bug-related dermatitis, allowing you to effectively address the issue.
Additionally, you’ll explore various methods of managing and treating dermatitis, ensuring that you’re equipped with evidence-based strategies to alleviate discomfort and promote healing.
Understanding dermatitis caused by bed bug infestations
Contrary to popular belief, the itchy red bumps on your skin may not solely be a result of bed bug bites, but rather a form of dermatitis caused by their infestations.
Bed bugs are small, blood-sucking insects that infest human dwellings, and their bites can lead to various skin reactions. However, recent studies have shown that it’s not the direct bite of the bed bug that causes the skin irritation, but rather the saliva they inject during feeding.
This saliva contains proteins that can trigger an allergic reaction in some individuals, leading to dermatitis. The severity of the dermatitis can vary, ranging from mild redness and itching to more severe cases with blistering and oozing.
It’s crucial to properly diagnose and treat this condition to alleviate discomfort and prevent further infestations.
Identifying symptoms and triggers of bed bug-related dermatitis
One key aspect to understand about bed bug-related dermatitis is that identifying the symptoms and triggers can help in effectively managing the condition.
Bed bug bites often result in itchy, red, and swollen skin lesions. These lesions may appear in a linear pattern or in clusters and are commonly found on exposed areas of the body, such as the face, neck, arms, and legs.
In some cases, bed bug bites can cause a severe allergic reaction known as systemic reactions, which may include fever, nausea, and difficulty breathing.
It is important to note that bed bug infestations can trigger dermatitis flare-ups in individuals who are already prone to skin conditions, such as eczema or psoriasis.
Therefore, it is crucial to identify and eliminate the bed bug infestation to prevent further dermatological complications.
Managing and treating dermatitis
Now that you’ve identified the symptoms and triggers of bed bug-related dermatitis, it’s crucial to understand how to manage and treat this condition effectively.
Managing dermatitis caused by bed bug bites involves both short-term relief and long-term prevention.
In the short-term, it’s essential to alleviate symptoms such as itching and inflammation. Over-the-counter topical creams containing corticosteroids can provide relief by reducing inflammation and itching. Antihistamines can also be used to alleviate itching and promote better sleep. Additionally, keeping the affected area clean and applying cold compresses can help reduce swelling.
Long-term prevention involves addressing the root cause of the infestation. This may include hiring professional exterminators to eliminate bed bugs from your home and taking preventive measures, such as regularly vacuuming, using mattress encasements, and sealing cracks and crevices.
By adopting these management and treatment strategies, you can effectively deal with bed bug-related dermatitis and improve your overall well-being.
Preventing Bed Bug Infestations
To effectively combat the relentless creep of bed bug infestations, it’s crucial for everyone to take proactive measures. Bed bugs are notorious for hitchhiking and can infest homes, hotels, and even public transportation.
Prevention is key to avoiding the discomfort and potential health risks associated with these pesky pests. Start by regularly inspecting your sleeping quarters, including the mattress, box spring, and headboard, for any signs of bed bugs, such as their excrement or shed skins. Encase your mattress and box spring in bed bug-proof covers to prevent them from infesting these areas.
When traveling, inspect hotel rooms thoroughly before settling in. Keep your luggage elevated and away from the bed, as bed bugs are more likely to be found near sleeping areas.
Lastly, be cautious when acquiring used furniture or clothing, as these can also harbor bed bugs. By following these steps, you can significantly reduce the risk of bed bug infestations and protect your skin from their irritating bites.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I tell if my skin condition is caused by bed bug bites or another factor?
To determine if your skin condition is caused by bed bug bites or another factor, look for a pattern of itchy, red bumps in groups or lines. Examine your sleeping area for signs of bed bugs such as blood stains or fecal spots. Consult a dermatologist for a proper diagnosis.
Can bed bug bites lead to more serious health problems?
Bed bug bites can lead to more serious health problems such as allergic reactions, skin infections, and psychological distress. It is crucial to seek medical attention and address the infestation promptly to avoid these complications.
How long does it take for bed bug bites to heal?
Bed bug bites typically heal within 1-2 weeks, but the duration can vary based on individual factors. Symptoms may be alleviated with over-the-counter creams or antihistamines. Seek medical attention if severe itching, swelling, or infection occurs.
Are certain individuals more prone to allergic reactions to bed bugs?
Yes, certain individuals may be more prone to allergic reactions to bed bugs. Factors such as genetics, previous exposure, and immune system response can influence the severity of reactions to bed bug bites.
What steps can I take to prevent bed bug infestations in my home?
To prevent bed bug infestations in your home, take the following steps: regularly inspect your bedding and furniture for signs of bed bugs, wash and dry your bedding on high heat, vacuum regularly, seal cracks and crevices, and avoid bringing used furniture into your home without thoroughly inspecting it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the role of bed bugs in dermatological conditions is crucial for effective prevention and treatment.
Bed bug bites can cause allergic reactions, leading to skin infections and dermatitis.
By identifying and addressing bed bug infestations promptly, the risk of these conditions can be minimized.
It’s important to implement preventive measures such as regular cleaning, vacuuming, and using protective covers for mattresses and pillows.
Additionally, early intervention and consultation with dermatologists can help manage any skin issues caused by bed bugs.